
reduced as far as possible, so 2/64 becomes 1/32 for instance. The fractions used are always in their simplest form, i.e. Most commonly used in the US, but can still be found occasionally in the UK, these imperial measurement drill bits come in 1/64 inch increments. Gaugeįractional drill bits are definedby the ANSI B94.11M-1979 standard.

The drill size chart below contains imperial and metric drill bit diameter measurements for all number and letter gauges. Most other countries, especially in Europe, have abandoned them entirely in favour of metric systems. They are also seen in the UK to a lesser degree, having been largely replaced by metric sizes. They are loosely based on the Stubs Steel Wire Gauge, with gauge sizes that are similar (but not entirely identical) to that system.Īlthough they originated in the 19 thcentury, these gauges are still commonly used in the U.S. Number and letter gauges do not follow a formula or standard increments.
#Drill size chart series
#Drill size chart full
The below video provides a short explanation of the threading termsĬlick the Thread Link to get the Full Thread Data for all classes All dimensions are in inches.To measure the diameter of a drill bit, it’s best to measure the cutting edge rather than the shank (the shank is the part that is held by the drill chuck). Major (Basic) diameter of external thread Major diameter, rounded root, internal thread For example: 3/4– 0.0625 P – 0.1875 L UNF denotes a 3/4″ UNF thread with 3 starts. For a multiple-start thread, the lead is also indicated.
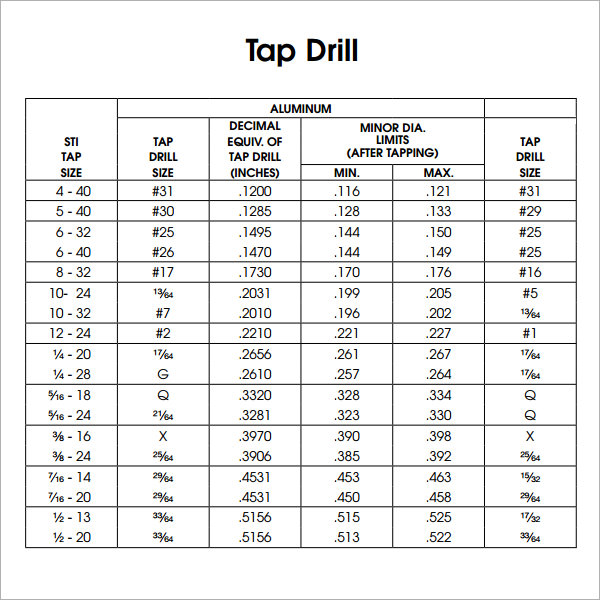
For a detailed explanation of classes, read the dedicated section below.1=Tight fit, 2=Medium fit, and 3=Loose fit. The first character is a digit between 1 and 3.The class is defined by a two-character code.The pitch remains the same for the whole diameter range in these series. ASTM B1.1, also defines several constant pitch series.In most cases, the series will be UN C, UN F, or UN EF (Coarse, Fine, or Extra fine pitch).For example, 1/4-0.05P means a thread with a pitch of 0.05″ (same as 20 TPI). It is also allowed to denote the pitch by distance.For example, 1/4-20 means a thread with a pitch of 20 TPI (1/20=0.05″). By default, the pitch is given in TPI.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
