
To force the mv command to not overwrite existing files when moving or renaming a file, use the -n flag. mv -v student1.txt student2.txt Do Not Overwrite Existing Files This flag enabled verbosity, which is helpful for auditing. To instruct the mv command to print out a log of actions being taken, you can use the -v flag. No output will be printed to the screen while files or directories are being moved or renamed. The mv command will perform its operations silently. mv /dir/1 /dir/2 /dir/3 /target/path Verbose Output Flag We simply specially all of the directories to be moved, and then give a target directory for them to be moved to. mv /tmp/logs ~/data/logsĪs with files, multiple directories can be moved to a new location. mv source-directory target-directoryįor example, to move a directory path /tmp/logs to ~/data/logs you would run the following command. We specify the source directory and give a target directory. Moving directories work the same as moving files. mv student1.txt student2.txt /var/students Moving Directories on Linux mv source-file-1 source-file-2 target-pathįor example, to move student1.txt and student2.txt to /var/students, you would run the following command. The last path will be treated as the target. When executing the mv command, each file listed will be considered a source with the last path being the exception. The mv command accepts multiple source files, which means we can move two or more files at the same time. mv student1.txt /var/students/class1-student1.txt Moving Multiple files on Linux mv old-filename /new/path/new-filenameįor example, to move a file named student1.txt to /var/students and rename it to class1-student1.txt, you would run the following command. When mv moves the file, it will be given a new name. You simply give the target path a different name. mv /home/student1/lab-work.log /var/labs/student1/lab-work.log Moving and Renaming files on LinuxĪ file can be renamed during a move process using the mv command. mv source-file /new/pathįor example, to move a file from /home/student1/lab-work.log to /var/labs/student1/lab-work.log, you would run the following command.

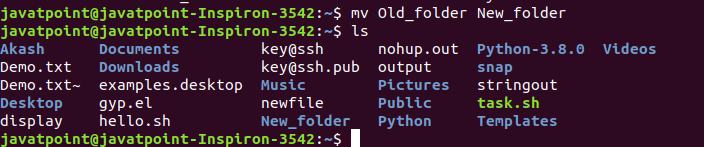
To move a file to another location we use the same method as renaming a file, except the file path should be different. Provided the file target is the same directory, all file attributes will remain, including permissions. To rename a file named student1 to student10, for example, you would run the following command. The mv command will take the source file specified and rename it to the target file. For renaming files, only two arguments are needed, which are the source file and the target file. The command accepts two or more arguments. To rename a file in Linux you use the mv command.

This means the operations done on one can be also done on the other, with very few exceptions.Īs such, you will notice that commands used to perform actions on files are identical with directories.
#Rename linux how to
Now you should know how to rename files on your Linux server.In this tutorial, you will learn how to use the mv command to move and renames files and directories on Linux.įiles and directories on Linux as very similar, from a filesystem point of view. jpg.Ī more common example is renaming files’ extensions from all-uppercase to all-lowercase rename 's/\.JPG$/.jpg/' *Īnd that’s it. Here’s a basic example of the rename command: rename 's/\.htm$/.html/' * However, this is for advanced users only. If you want to rename more files at once (in batches) you can use the “rename” command. In that case, you can use the “-i” option, which will ask you if you want to overwrite the file.Īs an example, if you already have an “index.php” file in the directory, and you want to rename “new.php” to “index.php”, you can use: mv -i new.php index.phpĪnd confirm when it asks you if you want to overwrite “index.php”.īatch files renaming using the rename command When you’re renaming files, chances are that you may rename the file to an already existing filename in the same directory. If they are in a different directory, you can use: sudo mv /path/to/file.old /path/to/file.new The commands above only work if the file is in the directory you’re currently in.
#Rename linux install
Here’s the syntax: mv oldfilename newfilenameĪnd here’s a real-life example that you’ll probably need to use after you install WordPress: mv wp-config-example.php wp-config.php The most basic (and relatively easiest) way of renaming commands in Linux is by using the mv command.
#Rename linux series
This is our fist tutorial in a series of quick and short Linux tutorials. Most commonly these commands are used on cloud servers and work on most Unix-based systems, including CentOS and Ubuntu. In this short tutorial, we’ll show you how to rename a file in Linux.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
